TIN-SLT
Published:
发表会议:North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL 2022)
第一作者:Yong Cao (PhD in HUST)
Question
如何解决 Sign Language Gloss Translation (SLGT) 的数据缺乏和 gloss 与 sentence 的表征空间不同的问题
Method
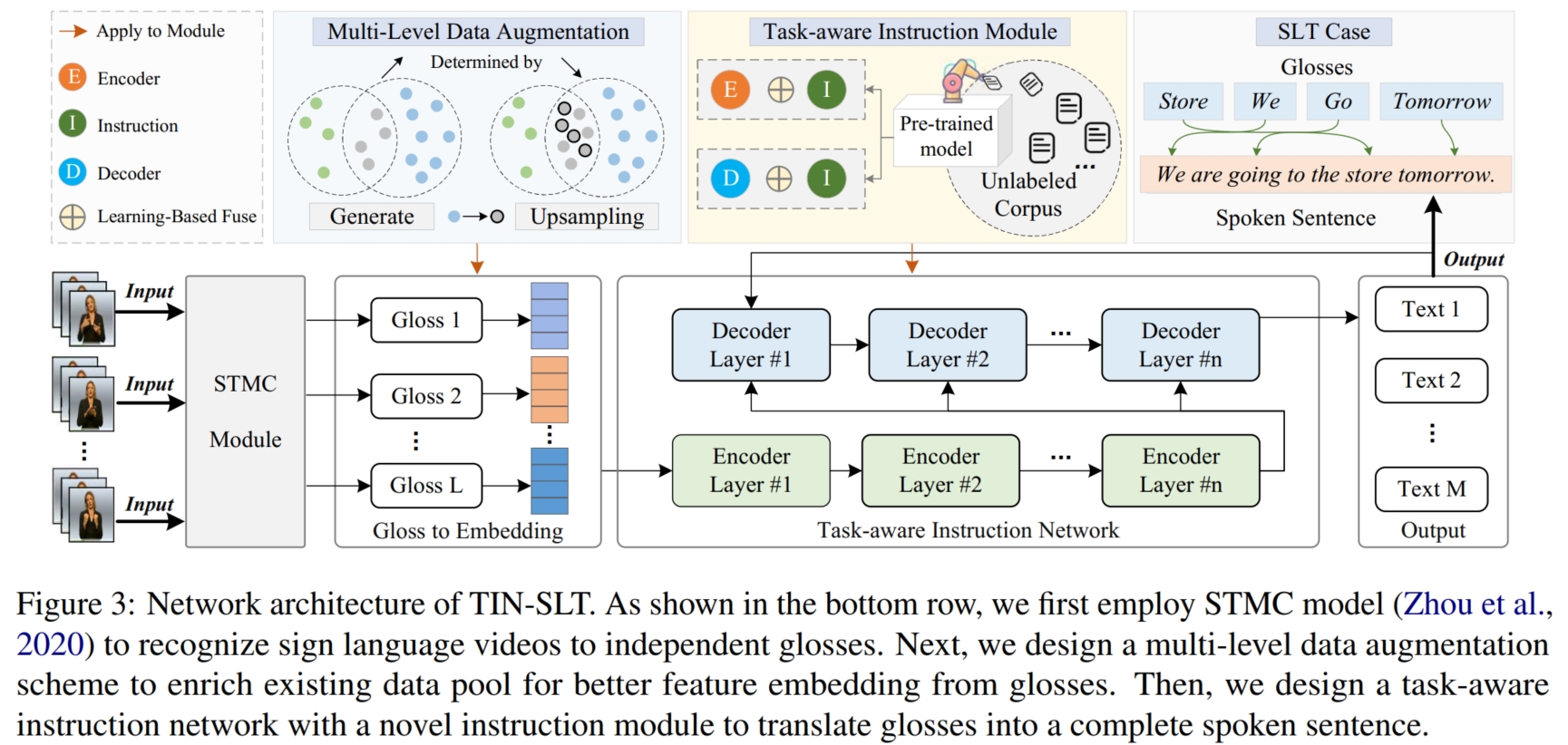
在如今大模型的时代下,最常见,也是最有效的解决数据缺乏的方法之一便是借助预训练的大模型。 如上图,本文便是将大模型编码得到的 embeddings 作为辅助信息使得模型能够学习到大模型的编码性能。 同时,为了解决表征空间差异问题,本文使用简单的上采样方法进行数据增强将 gloss 对齐到 sentence 空间。
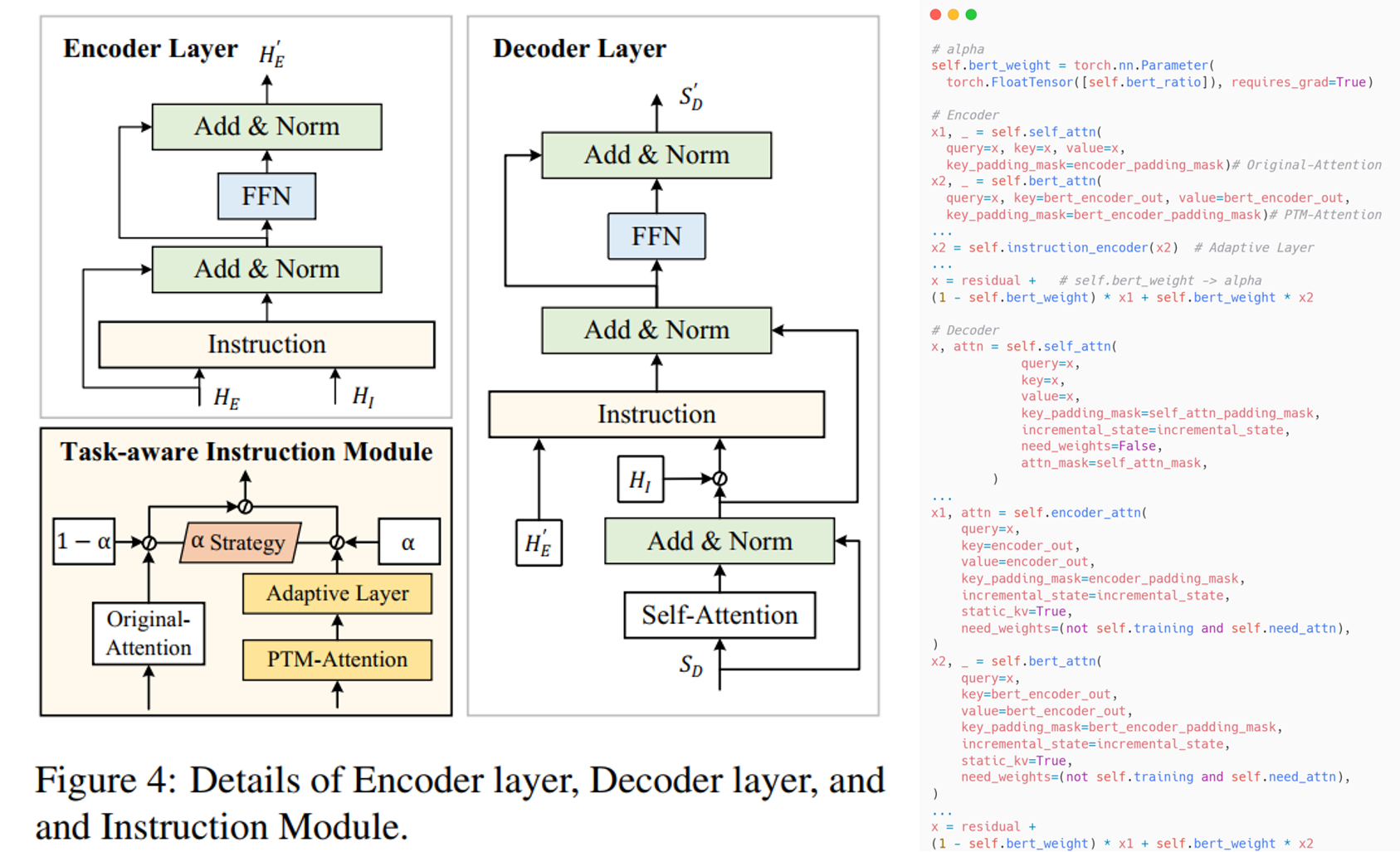
具体而言,如上图,本文使用的整体框架是 Transformer 的 Encoder-Decoder 框架。 假设数据集为 $D_o$,其中输入为 $\mathcal{G} = \{g_1,...,g_L\}$,输出为 $\mathcal{S} = \{\mathcal{w}_1,...,\mathcal{w}_M\}$。 为了将大模型的编码性能迁移到自身模型,本文提出了一个 Target-aware Instruction (TIM)模块嵌入 Encoder 和 Decoder 来帮助模型更好地学习。 TIM 的整体框架如图,包括一个 Original-Attention,一个 PTM-Attention,一个 Adaptive Layer 和一个 $\alpha$ 融合策略。 它包括 $3$ 个输入 $H_1$,$H_2$ 和 $H_3$,其中,$H_1$ 和 $H_2$ 是模型内部学习到的特征, 经过 Original-Attention (是一个 Cross-Attention)进行内部信息交叉学习更新:$\hat{h}_t^1 = Attn_O(h_t^1,H_2,H_2), H_1 = [h_1^1,...,h_T^1], \hat{H}_1 = [\hat{h}_1^1,...,\hat{h}_T^1]$。 而 $H_3$ 是外部的辅助信息(即大模型编码生成的 embeddings),经过 PTM-Attention (也是一个 Cross-Attention)进行外部信息交叉学习更新, 然后使用 Adaptive Layer (本文使用一个线性层) 对更新后的特征进行进一步更新学习, 使其学习到 target-aware 的特征:$\hat{h}_t^3 = \sigma(Attn_P(h_t^1,H_3,H_3)), \hat{H}_3 = [\hat{h}_1^3,...,\hat{h}_T^3]$。 最后使用 $\alpha$ 融合策略将二者进行融合输出更新的 $\bar{H}_1$:$\bar{H}_1 = (1 - \alpha) \times \hat{H}_1 + \alpha \times \hat{H}_3$。
在 Encoder 中,假设 $H_I$ 为大模型编码生成的 embeddings,$H_E$ 和 $H_E'$ 分别为 Encoder 的输入和输出。 本文将原本的 MHA 替换成了 TIM,且 TIM 中的 $H_1 = H_E, H_2 = H_E, H_3 = H_I$ (即Encoder 的 TIM 的 Original-Attention 是 Self-Attention), 然后 TIM 输出得到的 $\bar{H}_1$ 再经过一个 FFN 和 两次 Add & Norm 生成输出 $H_E'$:
在 Decoder 中,假设 $S_D$ 和 $S_D'$ 分别为 Decoder 的输入和输出。 本文将原本的 cross-MHA 替换成了 TIM。首先,输入 $S_D$ 经过一个 Mask-MHA,生成 $\tilde{S}_D$:
然后经过 TIM,TIM 中的 $H_1 = \tilde{S}_D, H_2 = H_E', H_3 = H_I$。 接着 TIM 输出得到的 $\bar{H}_1$ 再经过一个 FFN 和 两次 Add & Norm 生成输出 $S_D'$:
如上图右边代码,对于融合系数 $\alpha$,本文采用模型自我学习的方式,即将 $\alpha$ 设置为可学习的参数,随着模型的训练逐步更新。

为了解决表征空间差异问题,本文使用上采样进行数据增强,并实现将 gloss 对齐到 sentence 空间。 具体而言,如上图代码,本文通过设置一个阈值 $\Phi_{upsamp}$,使用概率选择在优质候选数据集 $\mathcal{C}$ 中进行随机选择,生成一个新数据集 $D_n$:
该新数据集中的输入和输出数据均为 sentence,则就使得模型学习 gloss 和 sentence 的空间对齐。 同时为了获得合适的阈值 $\Phi_{upsamp}$,本文综合考虑数据集 $D_o$、数据 $\mathcal{G}^i/\mathcal{S}^i$ 和数据元素 $g_i/\mathcal{w}_i$ 的差异来进行抉择。 具体而言,本文考虑了四方面的因素:
Token Level 1:Vocabulary Difference Ratio (VDR, $\phi_v$),用来测量 gloss 和 sentence 的字典空间的差异性:
$\phi_v = 1 - \dfrac{|W_\mathcal{G}|}{|W_\mathcal{G} \bigcup W_\mathcal{S}|}$ 其中,$W_\mathcal{G}$ 和 $W_\mathcal{S}$ 分别表示 gloss 和 sentence 的字典集。$|·|$ 表示大小。
Token Level 2:Rare Vocabulary Ratio (RVR, $\phi_r$),用来测量 gloss 中的生僻词的比例:
$\phi_r = 1 - \dfrac{\sum_{\mathcal{G} \in W_{\mathcal{G}}} U(Counter(\mathcal{G}) < \tau_r)}{|W_\mathcal{G} \bigcup W_\mathcal{S}|}$ 其中,$U(·)$ 表示 $1$ 如果内部表达式为真,反之则为 $0$。$Counter(\mathcal{G})$ 表示 $\mathcal{G}$ 的出现频率。
Sentence Level 1:Sentence Cover Ratio (SCR, $\phi_s$),用来测量总体 gloss-sentence 对的相似性:
$r_i = \dfrac{|\mathcal{G}_i \bigcap \mathcal{S}_i|}{|\mathcal{S}_i|},\ \phi_s = 1 - \dfrac{1}{N}\sum_{i, r_i > \tau_c}r_i$ 其中,$r_i$ 表示 gloss-sentence 对 $\{\mathcal{G}_i, \mathcal{S}_i\}$ 的相似性。 $\tau_c$ 表示 相似度阈值。此外,我们将所有相似度大于阈值 $\tau_c$ 的数据作为上采样的候选数据 $\mathcal{C}$。
Dataset Level 1:Dataset Length-difference Ratio (DLR, $\phi_d$),用来测量总体 gloss-sentence 对的长度差异:
$\phi_d = 1 - \dfrac{\sum_i{|\mathcal{G}_i|}}{\sum_i{|\mathcal{S}_i}|}$
最后,使用不同的比例 $\theta = [0.1,0.1,0.6,0.2]$ 来对这 $4$ 个指标进行加权, 生成最后的阈值 $\Phi_{upsamp} = \theta * [\phi_v,\phi_r,\phi_s,\phi_d]$,并使用上采样算法(公式 $(1)$)对 $\mathcal{C}$ 进行采样生成数据集 $D_n$。 最后将原始数据集 $D_o$ 和生成数据集 $D_n$ 进行合并,一起作为数据集对模型进行训练。